The digital transformation across industries is accelerating, and 3D texturing is poised to play an essential role in shaping the future of digital art, game development, visual effects, virtual reality, and product design. As we look ahead to 2030, educational trends in 3D texturing are evolving in tandem with technological advancements, making skill development crucial for professionals and students alike. This article explores how these trends will impact the industry and provides three detailed examples of success stories that demonstrate the transformative potential of 3D texturing.
Table of Contents
Industry Impact of 3D Texturing Technologies
In the coming decade, 3D texturing technologies are expected to revolutionize various sectors. From realistic simulations in VR and AR to seamless textures in video games and films, the precise detailing made possible by 3D texturing is driving innovation across creative and commercial industries.
One of the key educational trends is the growing adoption of procedural texturing techniques. These approaches enable artists to create realistic textures through algorithms rather than manually crafting every detail. Procedural tools allow artists to generate complex surfaces, such as weathered metals, natural materials, and even intricate cloth patterns, in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods. This means that 3D professionals can focus more on the creative aspects rather than technical labor, making them more productive and creative problem solvers.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in 3D texturing tools is transforming workflows. AI-assisted texturing automates repetitive tasks, predicts surface textures, and even provides suggestions for optimizing designs. Educational programs are increasingly incorporating AI-driven tools, giving students access to powerful resources that enhance their artistic capabilities and operational efficiency.
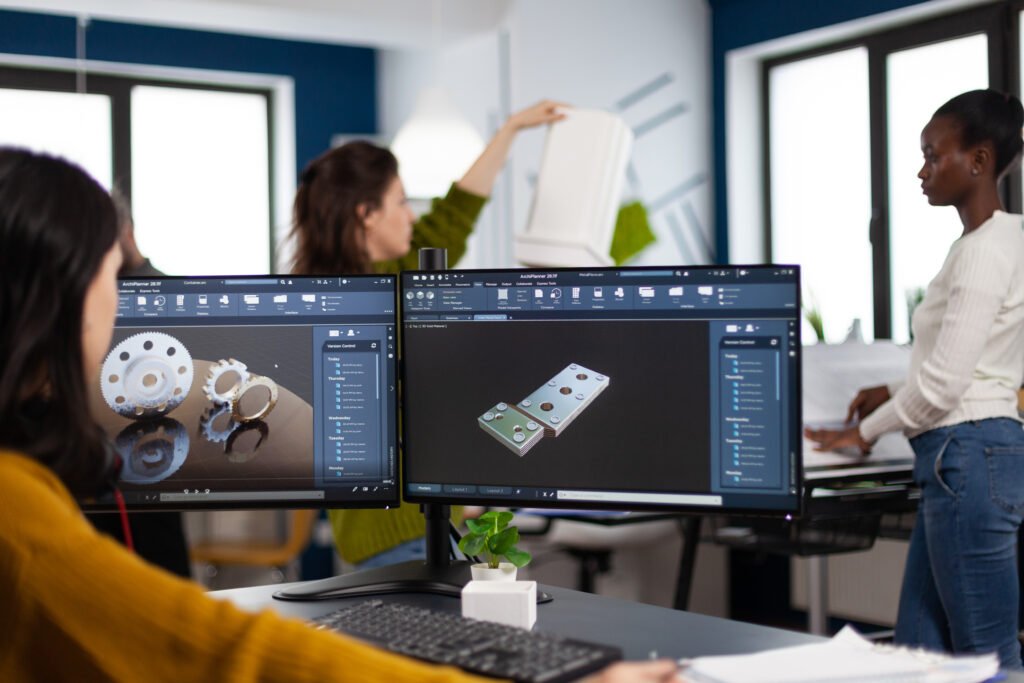

Benefits of 3D Texturing in Industry
The impact of 3D texturing goes beyond creative disciplines. In industries such as architecture, product design, and virtual marketing, the ability to visualize and manipulate high-quality textures can drastically improve communication, reduce prototyping costs, and speed up the production process.
For example, in the automotive industry, high-fidelity textures are used to simulate realistic car interiors and exteriors for virtual prototypes. This not only helps designers iterate more quickly but also allows marketing teams to create immersive experiences for customers before the physical product is even available. 3D texturing has helped companies achieve more significant precision in their digital assets, leading to better decision-making and faster market entry.
In the field of education, the rise of online learning platforms focused on 3D design and texturing is making these skills more accessible to a broader audience. Platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and specialized courses from leading software developers like Adobe and Autodesk are enabling students to learn at their own pace. These courses include hands-on experiences, where learners can interact with tools like Substance Painter and Designer, bridging the gap between theory and practice.

3D Texturing Success Stories
1. Epic Games: Procedural Texturing in Video Game Development
One of the most notable success stories is from Epic Games, the creators of the Unreal Engine. With the introduction of Unreal Engine 5, Epic Games showcased how procedural texturing can significantly enhance video game environments. For instance, the dynamic environments in Fortnite and other AAA titles are built using procedural techniques that enable designers to create vast landscapes and terrains with minimal manual intervention.
By automating texture generation, Epic Games’ team can focus more on gameplay mechanics and artistic direction, delivering breathtaking visual experiences without compromising efficiency. The success of Unreal Engine 5 has also influenced many other game development studios to adopt similar techniques, pushing the boundaries of what’s visually achievable in video games.
2. Tesla: 3D Texturing in Automotive Design
Tesla has utilized 3D texturing to revolutionize the way vehicles are designed and presented to customers. Through advanced texture-mapping techniques, Tesla has been able to create highly realistic simulations of their cars’ interiors and exteriors. This approach allows them to iterate faster in the design phase while creating compelling virtual demonstrations for customers.
The ability to simulate textures down to the finest details, such as leather seats or metallic finishes, has enabled Tesla to create more engaging marketing materials, including virtual showrooms. Their use of high-fidelity textures in both product design and customer experiences demonstrates how 3D texturing can blend creativity with functionality to drive business transformation.
3. Disney: Realism in Animated Films
Another prime example of the industry impact of 3D texturing is seen in Disney’s animated films. Movies like Raya and the Last Dragon and Encanto showcase stunning environments that rely on advanced texturing techniques. Disney’s use of procedural texturing and AI-driven tools allowed artists to create realistic surfaces for natural environments, water, and complex fabrics while maintaining a hand-crafted aesthetic.
The success of these films lies not only in their engaging storytelling but also in their technical brilliance. By leveraging innovative texturing methods, Disney has maintained its reputation for creating magical, immersive worlds that capture audiences’ attention.
Innovative Use of 3D Texturing in Education
As the demand for high-quality textures grows, educational institutions are rethinking how they teach 3D texturing. One trend gaining traction is the use of VR and AR tools to teach texture creation. These immersive learning environments allow students to engage with 3D objects and manipulate textures in real-time, offering a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and surface details.
Furthermore, collaborative platforms that allow students and professionals to work together in virtual spaces are emerging. This global accessibility helps students from different parts of the world engage with industry professionals and work on real-world projects, accelerating their skill development and preparing them for future careers.
Another educational trend is the gamification of learning, where students can practice 3D texturing through game-like environments. This makes learning more interactive and engaging, keeping students motivated to refine their skills.

The Future of Skill Development in 3D Texturing
By 2030, the continuous advancement of 3D texturing tools will create new opportunities for artists, designers, and engineers across industries. The growing integration of procedural texturing, AI-driven solutions, and immersive education tools will streamline workflows, enhance creativity, and lead to more realistic and dynamic digital environments.
Educational institutions that incorporate these cutting-edge technologies into their curriculums will play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of skilled professionals, ensuring that industries have the talent they need to meet future challenges.
With years of expertise in this technology, we are here to support your needs. If you’re interested in learning more about similar technologies and how they can be applied, feel free to reach out to our team at . You can also connect with us via LinkedIn at or reach our support team on WhatsApp at .






